Definition of Corneal Abrasion
A corneal abrasion, often referred to as a scratched cornea or scratched eye, is a common and painful injury involving a scratch on the surface of the eye, specifically the cornea. The cornea is the clear, protective outer layer of the eye that helps focus light onto the retina, and when this layer is scratched, it can lead to discomfort and potential complications if not treated properly.
The Importance of Seeing an Eye Doctor to Promote Healing and Prevent Infections
It is crucial to seek prompt evaluation by an eye doctor if you suspect a corneal abrasion. Delay in treatment can lead to complications, such as:
- Infections: An open wound on the cornea is susceptible to infections that can threaten vision.
- Recurrent Corneal Erosions: Improper healing can lead to recurrent abrasions that cause ongoing pain.
- Visual Impairment: Poorly healed abrasions can obscure vision or lead to scarring, impacting quality of life.
During an evaluation, our eye doctors can accurately diagnose the extent of the abrasion using specialized tools, such as a slit lamp, and may apply a fluorescent dye to highlight the scratch. Treatment options can include antibiotic eye drops to prevent infections, lubricating eye ointments for comfort, and possibly a temporary patch or bandage contact lens to promote healing and alleviate pain. Early treatment typically means healing occurs within a few days, minimizing potential long-term effects.

Emergency Response and Treatment
In the event of a suspected corneal laceration, immediate medical attention is essential. Here’s what to do:
- Carefully cover the injured eye with a sterile shield or cup until you can see an eye doctor. Avoid pressing on the eye.
- Do not rinse the eye with water or attempt to remove any foreign objects; this can worsen the injury.
- Refrain from rubbing the eye, as this can cause further damage and complications.
- Avoid taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen or aspirin, which might increase bleeding and complications.
Upon arrival at our eye care clinic in Costa Mesa, our eye doctor will conduct a thorough examination, possibly utilizing a fluorescein stain to assess the extent of the injury. Treatment may involve surgical intervention to repair the laceration, remove debris, and prevent infections. Depending on the severity of the laceration and the underlying trauma, follow-up care and monitoring will be crucial. Healing times vary; however, deeper lacerations may take longer to resolve and could necessitate further treatments or therapies.
Symptoms of Corneal Abrasion
Physical Discomfort and Pain
A corneal abrasion, often described as a scratched eye, can lead to significant discomfort and sharp pain. Patients frequently report a sensation as if something is caught in their eye, a feeling intensified by the cornea’s dense network of nerve endings. These pain receptors make any injury to the cornea extraordinarily painful, often akin to stabbing sensations. This discomfort can range from mild irritation to severe, debilitating pain, making daily activities challenging, particularly for children who may struggle to articulate their discomfort.
Vision-related Symptoms
Corneal abrasions can cause various vision-related issues. Common symptoms include:
- Blurry or hazy vision
- Increased sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Excessive tearing or watery eyes
- Redness in the eye
These symptoms can greatly affect both children and adults. In particular, children may close or squint their eyes often, indicating discomfort and aversion to light, which can be especially distressing for parents trying to understand what their child is experiencing. If left untreated, these symptoms can evolve, leading to potential complications like recurrent corneal erosions, which may cause further distress if they persist.
Other Possible Indications
In addition to physical pain and vision issues, individuals with corneal abrasions may also experience:
- Frequent blinking or spasms in the affected eye
- Nausea or headaches due to intense discomfort
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial in preventing complications such as secondary infections and scarring that can impact long-term vision. Symptoms can sometimes mirror other eye conditions; therefore, only professional examination can confirm the injury.
Home Care Essentials
While medical treatment is vital, you can also take steps at home to support healing while you wait for your appointment or between follow up visits:
- Avoid Rubbing Your Eyes: Resist the urge to rub or touch the affected eye, as this can exacerbate the injury and hinder healing.
- Use Cold Compresses: Applying a clean, cold compress can help alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
- Sunglasses for Light Sensitivity: Wear sunglasses outdoors to protect your eyes from bright light, which can worsen discomfort.
- Minimize Screen Time: Reduce the use of screens during the healing process to avoid eye strain.
- Keep Follow-Up Appointments: Adhere to your eye doctor’s recommendations for follow-ups to ensure proper healing.
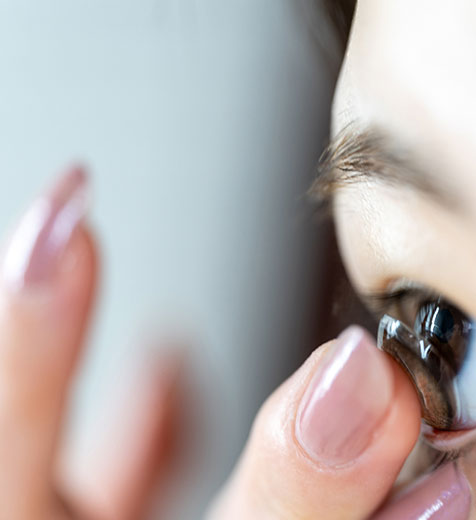
Special Considerations for Contact Lens Wearers
If you or your child wear contact lenses, extra caution should be exercised. Contact lenses can sometimes increase the risk of corneal abrasions, particularly if they are not fitted properly or if they are worn beyond the recommended time frame. Here are some important points to consider:
- Remove Lenses: Contact lenses should be removed immediately if a corneal abrasion occurs, and you should refrain from wearing them until your eye has healed completely.
- Choose the Right Lenses: Discuss with your eye care provider the best type of contact lenses for your eyes and lifestyle to minimize the risk of future abrasions.
- Regular Check-Ups: Maintain regular eye exams to ensure your contact lenses fit properly and to evaluate your overall eye health.
By adhering to these recommendations, you can help reduce the likelihood of recurrent abrasions and ensure a smoother healing process. Remember, your eye health is critical, and taking the proper steps after a corneal abrasion can lead to a quicker return to your normal activities.

Importance of the Cornea in Vision
The cornea is critical for clear vision, serving as the eye’s outermost lens. It helps to focus light and contributes significantly to quality vision. Any disruption, such as a corneal abrasion, can lead to symptoms like blurriness, light sensitivity, and a sensation of a foreign body in the eye. Moreover, the cornea is equipped with a dense network of nerve fibers, making abrasions particularly painful.
Why Are Corneal Abrasions Painful?
Nerve Structure of the Cornea
The cornea is one of the most sensitive tissues in the human body, containing an exceptionally high density of nerve fibers—about 500 times more than the skin. These nerves serve a protective function, alerting us to potential injury. When a corneal abrasion occurs, the exposed nerve endings become activated, leading to intense sensations of pain and discomfort. This is the human body’s natural response, as pain signals help prevent further injury by encouraging protective behaviors, such as blinking or avoiding rubbing the eye.
Causes and Risk Factors for Corneal Abrasion
Common Causes of Corneal Abrasion
Corneal abrasions can occur from various everyday activities and accidents. Common causes include:
- Fingernails scratching the eye, often seen in children who may poke their eyes during play or while getting too close to others.
- Makeup brushes or application tools that come into contact with the eye.
- Foreign objects like dust, sand, or dirt, especially when rubbing the eyes.
- Tree branches or other environmental hazards, particularly during outdoor activities.
- Improper handling of contact lenses, which can cause scrapes during insertion or removal.
Even seemingly minor incidents can lead to significant discomfort, as the cornea’s sensitivity makes even small abrasions feel quite severe.
Situational Risk Elements
Certain situations increase the likelihood of experiencing corneal abrasions. Engaging in activities such as yard work or home repairs without protective eyewear greatly raises the risk of injury. Additionally:
- Dry Eyes: Those suffering from chronic dry eye conditions may be more susceptible, particularly if their eyes dry out while sleeping, causing the eyelids to stick to the cornea.
- Rubbing the Eyes: This common reaction to irritation can exacerbate a situation, worsening an existing abrasion or causing a new one.
It’s important to recognize these situations to mitigate risks through proper precautions.
Occupational and Lifestyle Risks
Corneal abrasions are prevalent in various occupations and lifestyle activities, often occurring in environments where eye protection is not utilized. For instance:
- Workplace injuries: Approximately 25% of corneal abrasions occur at work, particularly in industries involving machinery, construction, or any scenario with small flying debris.
- Sports Participation: Athletes not wearing protective eyewear are at a higher risk of abrasions from sports-related incidents.
- Hobbies: Activities such as woodworking, metalworking, or even certain crafting hobbies can contribute to injuries if proper safety measures are ignored.
Treatment Options for Corneal Abrasion
If you or your child are experiencing a corneal abrasion, you may be feeling significant discomfort and anxiety. A scratched cornea can feel like having something stuck in your eye, and it often leads to light sensitivity, redness, and blurred vision. Understanding the treatment options available can help you feel more empowered and hopeful about recovery.
Medical Interventions
Your eye care provider will determine the appropriate treatment based on the severity of the abrasion. Treatments may include:
- Eye Patching: A patch or bandage may be placed over the injured eye to prevent blinking, thereby reducing pain and allowing the corneal epithelium to heal.
- Moisturizing Eye Drops: Prescribed eye drops or ointments can help soothe the eye and add a protective layer over the cornea, reducing discomfort.
- Antibiotic Drops: To prevent infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotic eye drops or ointment, especially if the abrasion is caused by a foreign material or if contact lenses were involved.
- Cycloplegic Eye Drops: These special drops can help relieve pain by temporarily dilating the pupil and reducing light sensitivity.
- Bandage Contact Lenses: In some cases, a bandage contact lens may be utilized to provide comfort and encourage faster healing.
Most corneal abrasions heal within 24 to 48 hours, although larger abrasions may take longer. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing progress.
Factors Affecting Healing Time
Size and Depth of Abrasion
The healing time for a corneal abrasion varies significantly depending on the size and depth of the injury. Smaller abrasions, typically affecting only the outer layer of the cornea known as the epithelium, usually heal within 1 to 2 days. In contrast, larger abrasions can take about a week or more to heal, especially if they penetrate deeper layers of the cornea. The cornea has an incredible ability to heal, but the depth of the wound plays a crucial role. For instance, abrasions affecting between 25% to 50% of the cornea may require more intensive treatment, and larger abrasions can lead to complications such as corneal edema, which may prolong the healing process significantly.
Patient-specific Factors
Individual patient characteristics can significantly influence the healing time of a corneal abrasion. Factors such as age, overall health, existing eye conditions (like dry eyes), and lifestyle can play a role. For example, children are particularly susceptible to developing corneal abrasions due to common play activities and roughhousing. Moreover, patients with conditions that cause dry eyes may experience a longer healing time due to the compromised surface environment of the cornea. Furthermore, improper contact lens wear and poor eye hygiene can lead to further complications, lengthening the recovery process.
Additionally, systemic health conditions like diabetes may slow down healing times and increase the risk of complications. Therefore, a tailored treatment plan focused on the individual patient’s needs helps promote optimal healing.
Risk of Complications and Recurrent Erosion
Corneal abrasions pose a risk of complications, particularly if not treated correctly or if the abrasion is severe. One of the most concerning outcomes is the development of recurrent corneal erosion (RCE). This occurs when the new epithelial layer does not attach firmly to the underlying corneal layers, often leading to repeated episodes of pain and discomfort. Patients with a prior history of corneal abrasions or pre-existing conditions such as corneal dystrophies are specifically at risk for RCE.
Infections are another significant risk associated with corneal abrasions. Although rare, a corneal abrasion creates an open wound that can become infected, especially if caused by organic material or if the patient does not adhere to the prescribed treatment plan. Symptoms of infection may include increased pain, redness, and vision changes. Early intervention and appropriate antibiotic treatment are crucial for preventing such complications.
We emphasize that if you or your child are experiencing persistent discomfort or notice any worsening symptoms following a corneal abrasion, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention. We are here to assist you with tailored treatment and thorough follow-up care to ensure optimal recovery outcomes.
Preventing Corneal Abrasions and Erosions
Protective Eyewear and Safety Tips
Corneal abrasions, or scratched corneas, can lead to severe pain and vision issues. Knowing how to prevent these injuries is crucial for maintaining eye health for both adults and children alike. Eye injuries often occur unexpectedly during routine activities, so taking proactive measures is essential. Here are some effective safety tips to help protect your eyes:
- Wear Protective Eyewear: Always use safety goggles or protective glasses when engaging in activities that pose a risk to your eyes. This includes yard work, using power tools, playing contact sports, or any activities that involve flying objects or debris.
- Pay Attention During Makeup Application: Be cautious when using makeup brushes or other items near your eyes. Accidental pokes or scrapes can easily result in an abrasion.
- Children’s Safety: Ensure that children are supervised during play. Use goggles when children participate in sports or when they engage in activities that involve sharp objects.
- Trimming Fingernails: Regularly trim your child’s nails to reduce the risk of them accidentally scratching their own eyes.
- Mind Your Surroundings: Be aware of your environment, particularly around trees and bushes. Trim overgrown branches that may be at eye level.
Proper Contact Lens Care
While contact lenses can enhance vision, improper use can increase the risk of corneal abrasions. Here are guidelines for proper contact lens care:
- Follow Usage Instructions: Make sure to adhere to the prescribed wearing schedule. Do not sleep in your contact lenses unless they are specifically designed for extended wear.
- Keep Lenses Clean: Replace your contact lens solution regularly and use the appropriate cleaning solutions recommended by your eye care provider to prevent infections and abrasions.
- Inspect Lenses for Damage: Always check for rough edges or tears in your lenses before use. Damaged lenses can easily scratch the surface of your eye.
- Maintain Eye Moisture: If you frequently experience dry eyes, it’s vital to address this issue with your eye doctor. Dry eyes can increase the risk of your eyelids sticking to the cornea and causing an abrasion when you blink.
Preventive Measures in Children
Children are particularly prone to corneal abrasions due to their increased activity levels and curiosity. To help prevent these injuries in younger patients, consider the following:
- Supervised Play: Always supervise children during playtime to prevent accidents. Be mindful of small objects that may get into their eyes.
- Education: Teach children to avoid rubbing their eyes, especially if they feel something is in there. Encourage them to use water to flush their eyes instead.
- Regular Eye Exams: Schedule routine eye check-ups to ensure that children’s vision and eye health are being monitored effectively.
- Use of Protective Gear: Make protective eyewear a habit in any sports or physical activity your child participates in.
By implementing these easy yet effective preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of corneal abrasions and erosions for both yourself and your children. If an injury does occur, timely medical attention from an eye care professional is essential for optimal recovery.
Managing Pain and Comfort
Pain Relief Strategies
A corneal abrasion can be extremely uncomfortable and painful, presenting symptoms such as a gritty sensation, redness, and sensitivity to light. Understanding how to manage this pain effectively is crucial for recovery. Here are a few strategies we recommend:
- Antibiotic Eye Drops: Following the initial diagnosis, antibiotic eye drops may be prescribed to prevent infection and minimize discomfort as your eye heals. These drops help protect the exposed corneal surface and provide a soothing effect.
- Pain Relief Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, may be suggested to alleviate pain associated with the scratch.
- Bandage Contact Lenses: In some cases, healing can be accelerated by using specialized bandage contact lenses. These lenses offer pain relief by covering the abrasion, allowing for more comfortable blinking.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up visits are often necessary to monitor your healing process and adjust treatment as needed. This ensures your recovery stays on track.
Role of Moisturizing Drops
Moisturizing drops, often referred to as artificial tears, play a vital role in the healing of corneal abrasions. They help:
- Provide instant comfort by lubricating the surface of the eye, thus reducing friction caused by blinking.
- Flush away irritants or foreign particles that could lead to further irritation or potential infection.
- Support the natural healing process by ensuring the corneal surface remains moist, which enhances the recovery of the epithelial layer.
- Minimize symptoms of dryness, which can exacerbate discomfort while your cornea heals.
It is important to use preservative-free drops, especially when your eye is sensitive, as preservatives can sometimes provoke irritation.
Importance of Avoiding Eye Rubbing
One of the most significant recommendations for anyone with a corneal abrasion is to avoid rubbing their eyes. Rubbing can:
- Exacerbate Symptoms: Rubbing the eye can lead to increased pain and discomfort, potentially worsening the abrasion or creating new injuries.
- Delay Healing: Every time you rub your eye, you risk interrupting the natural healing process of the cornea. This can prolong recovery and increase the likelihood of complications.
- Introduce Infection: Your hands can carry bacteria, which can be introduced to an open abrasion through rubbing, leading to serious complications.
Educating both children and adults about the risks of rubbing the eye is essential; using methods such as wearing sunglasses or eye shields can help deter this instinctive behavior during the healing process.
Corneal Lacerations vs. Abrasions
Definition and Severity of Lacerations
Understanding the difference between corneal abrasions and corneal lacerations is critical for both patients and healthcare providers. A corneal abrasion is a superficial scratch or scrape on the cornea, the clear front surface of the eye, primarily affecting the protective outer layer known as the epithelium. While abrasions can cause significant pain and discomfort due to the cornea’s high density of nerve endings, they typically heal quickly—within a few days to a week—without leading to severe complications.
In contrast, a corneal laceration is more serious, involving a deeper cut that may penetrate fully or partially through the cornea. This type of injury is often caused by high-impact trauma, such as blunt force or sharp objects. Lacerations present a higher risk of vision loss and may require immediate medical intervention to ensure the integrity of the eye is preserved. Clear signs of a laceration may include severe pain, changes in vision, or irregularities in the pupil shape and reaction.
Patient Stories: Real-life Experiences
Case Study: Emily’s Abrasion Journey | Irvine, CA
Emily, a 9-year-old, had a fun day at the park playing with friends when she suddenly felt a sharp pain in her eye after accidentally scratching it with a tree branch. Her parents noticed she was rubbing her eye incessantly and had trouble keeping it open because of the intense sensitivity to light. Upon visiting a local eye care provider, Emily was diagnosed with a corneal abrasion, which is often referred to as a scratched cornea.
After a thorough examination using a fluorescent dye and a specialized slit lamp, the ophthalmologist explained that Emily’s abrasion would quickly heal with the right treatment. She was prescribed antibiotic eye drops to prevent infection and eye ointment to ease discomfort. To help manage the pain, a patch was placed over her eye to allow it to rest and heal without the irritation from blinking.
After 48 hours of adhering to the treatment, Emily returned for a follow-up appointment. She was excited to learn that her eye had healed well, and her vision was restored without any complications. The doctor also discussed protective eyewear, emphasizing to Emily and her parents how these simple precautions can prevent future injuries.
Case Study: Dan’s Abrasion Journey | Costa Mesa, CA
During a weekend soccer match, 12-year-old Dan collided with another player and ended up with a scratched cornea from the impact of a fingernail. Dan’s symptoms included severe pain, tearing, and a persistent feeling of something being in his eye. His parents were worried when they noticed him squinting and avoiding bright lights.
Dan was brought to the clinic, where the eye doctor quickly diagnosed a corneal abrasion. The doctor, utilizing the fluorescein dye test, confirmed that the outer surface of Dan’s cornea had been scratched. After assessing the depth of the injury, he received a prescription for antibiotic eye drops to mitigate infection risks and was advised against any activities that might exacerbate the injury.
Following a couple of days of treatment, Dan felt a significant reduction in pain and was able to resume his activities with care. At his follow-up appointment, the doctor congratulated him on a successful recovery and reinforced the importance of eye safety during sports. Dan learned a valuable lesson about being mindful of his surroundings and is now committed to wearing protective goggles during games.
Schedule an Emergency Eye Exam for A Scratched Eye In Costa Mesa
Our state of the art medical eye care center provides advanced eye care and urgent care for eye emergencies for patients from Costa Mesa, Irvine, Orange, Huntington, and all of Orange County. If you or your child has scratched their eye, please call our office and we can provide you with specific advice tailored to your symptoms and needs.